10 Facts About Analytical Chemistry Technique That Will Instantly Put You In A Good Mood
Sneak Peak At What’s Next For Analytical Chemistry Testing

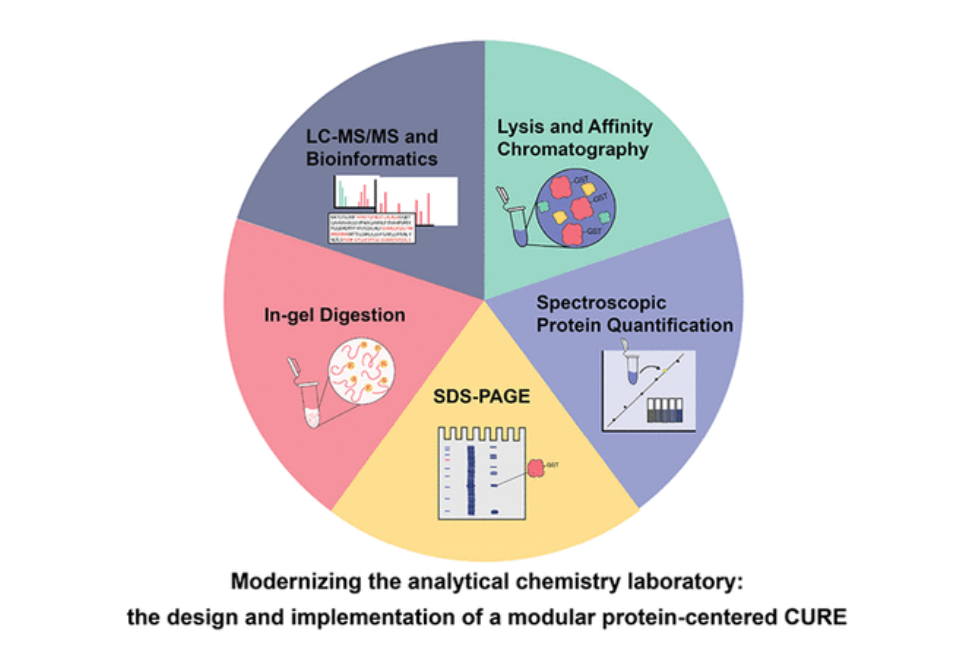
The majority of Analytical Chemists work for personal research and development firms, while another large part work for pharmaceutical companies or screening labs. * An analytical chemist task may look various depending on which field it is in, however from healthcare to petroleum, the analytical chemist will be required to manage chemical, physical, and analytical lab tests like titrations, acid/base functional group analyses, viscometry, water analyses and other screening of known and brand-new products.
Be prepared to present results to different stakeholders. Identify potential challenges and proactively strategy for resolution Build relationships throughout several cultures and regions to support advancement in the field Make sure that all reagents and solutions are prepared according to SOPs Guarantee that equipment is calibrated to validate accuracy, dependability and accuracy, Translate and document all test results including computations and observations in laboratory documents Evaluation peers’ analytical data for precision and integrity Alert the Chemist-in-charge of uncommon test results and of any troubles or problems experienced during the performance of tasks A managerial analytical chemist job may have these or comparable extra parts: Apply and communicate understanding of chemistry to company systems, partners, and the general public Improve technical leadership by training the workgroup, along with internal business partners and external customers Gain international recognition as a scientist with a detailed understanding of your field and the ability to communicate efficiently with international groups Manage process improvements and data quality to help group satisfy company and scientific criteria Create and deliver discussions to work group(s), consumers, and external organization contacts Develop a leadership function in industry-related activities Analytical Chemists require a bachelor’s degree in chemistry, physics, or other associated field just to obtain entry-level positions.
The majority of Analytical Chemists working in the research study field must acquire a master’s degree or Ph. D to advance. Specialization in the subfield of Analytical Chemistry is generally pursued throughout graduate education. Analytical Chemists can browse through these companies and websites for important resources: Federation of Analytical Chemistry and Spectroscopy Societies (FACSS) is a non-profit company that brings lots of different types of analytical scientists from around the world together to share ideas across disciplines.
The most recent news in the market becomes easily available to members in the form of short articles, videos, and other multimedia. system laboratory requirements. This publication can be incredibly useful for finding out more about analytical chemistry or staying upgraded on present industry patterns. [xyz_school_button * 2020 United States Bureau of Labor Statistics salary figures and job growth forecasts for Chemists reflect national data not school-specific details.
Learn Analytical Chemistry Techniques In Ten Minutes
The very first instrumental analysis was flame emissive spectrometry developed by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff who found rubidium (Rb) and caesium (Cs) in 1860. The majority of the significant developments in analytical chemistry happened after 1900. During this duration, critical analysis ended up being progressively dominant in the field. In specific, many of the basic spectroscopic and spectrometric strategies were discovered in the early 20th century and refined in the late 20th century.
In the 1970s a lot of these methods began to be used together as hybrid strategies to accomplish a total characterization of samples. Starting in the 1970s, analytical chemistry ended up being gradually more inclusive of biological questions (bioanalytical chemistry), whereas it had previously been largely focused on inorganic or small natural particles.
Modern analytical chemistry is controlled by important analysis. Many analytical chemists focus on a single type of instrument. Academics tend to either focus on brand-new applications and discoveries or on brand-new approaches of analysis.
Many methods, as soon as established, are kept purposely static so that data can be compared over long periods of time. (QA), forensic and ecological applications.
The existence of copper in this qualitative analysis is shown by the bluish-green color of the flame Although modern analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and a few of the concepts used in contemporary instruments are from traditional methods, numerous of which are still used today. what is analytical chemistry.
What Research Says About Chemistry Lab Setup
Qualitative analysis determines the existence or lack of a particular substance, but not the mass or concentration. By definition, qualitative analyses do not measure amount. Inorganic qualitative analysis typically refers to a systematic scheme to verify the existence of certain liquid ions or components by carrying out a series of responses that remove a range of possibilities and then validate believed ions with a confirming test.
The very first instrumental analysis was flame emissive spectrometry developed by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff who discovered rubidium (Rb) and caesium (Cs) in 1860. The majority of the major advancements in analytical chemistry happened after 1900. Throughout this period, important analysis ended up being gradually dominant in the field. In particular, much of the standard spectroscopic and spectrometric strategies were discovered in the early 20th century and fine-tuned in the late 20th century.
In the 1970s a lot of these methods started to be used together as hybrid strategies to accomplish a total characterization of samples – analytical chemistry skills. Beginning in the 1970s, analytical chemistry ended up being progressively more inclusive of biological questions (bioanalytical chemistry), whereas it had formerly been largely concentrated on inorganic or little natural molecules.
Modern analytical chemistry is dominated by instrumental analysis. Many analytical chemists focus on a single type of instrument. Academics tend to either focus on brand-new applications and discoveries or on new approaches of analysis.
An effort to develop a new approach might include making use of a tunable laser to increase the uniqueness and sensitivity of a spectrometric method. Lots of approaches, when established, are kept intentionally static so that information can be compared over long periods of time. This is especially real in commercial quality control (QA), forensic and ecological applications.
8 Laboratory Quality Management Hacks Only The Pros Know
The presence of copper in this qualitative analysis is indicated by the bluish-green color of the flame Although contemporary analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and some of the principles used in contemporary instruments are from conventional methods, a lot of which are still used today.
Qualitative analysis figures out the presence or absence of a specific compound, however not the mass or concentration. By definition, qualitative analyses do not determine quantity. Inorganic qualitative analysis normally refers to an organized plan to confirm the existence of specific liquid ions or aspects by performing a series of responses that remove a variety of possibilities and then confirm suspected ions with a validating test.
Most of the major developments in analytical chemistry took place after 1900. Throughout this period, crucial analysis became gradually dominant in the field. In particular, many of the basic spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques were discovered in the early 20th century and refined in the late 20th century.

In the 1970s a number of these techniques started to be utilized together as hybrid techniques to accomplish a total characterization of samples – example of analytical chemistry. Beginning in the 1970s, analytical chemistry ended up being progressively more inclusive of biological concerns (bioanalytical chemistry), whereas it had actually formerly been mainly focused on inorganic or small organic particles.
Modern analytical chemistry is dominated by important analysis. Lots of analytical chemists focus on a single type of instrument. Academics tend to either focus on brand-new applications and discoveries or on brand-new methods of analysis.
A Deep Dive Into Lab Space
Many approaches, once established, are kept deliberately fixed so that data can be compared over long durations of time. (QA), forensic and environmental applications – laboratory setting.
The presence of copper in this qualitative analysis is suggested by the bluish-green color of the flame Although contemporary analytical chemistry is controlled by advanced instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and a few of the principles utilized in contemporary instruments are from traditional methods, a lot of which are still utilized today – analytical chemistry lab techniques.
Qualitative analysis identifies the presence or absence of a particular compound, however not the mass or concentration. By meaning, qualitative analyses do not measure amount. Inorganic qualitative analysis usually refers to an organized plan to verify the presence of certain aqueous ions or elements by performing a series of reactions that eliminate a range of possibilities and then validate believed ions with a verifying test.
The very first crucial analysis was flame emissive spectrometry established by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff who discovered rubidium (Rb) and caesium (Cs) in 1860. The majority of the major advancements in analytical chemistry took location after 1900. Throughout this period, important analysis ended up being gradually dominant in the field. In particular, a number of the standard spectroscopic and spectrometric strategies were found in the early 20th century and refined in the late 20th century.

In the 1970s a lot of these techniques started to be utilized together as hybrid strategies to accomplish a total characterization of samples. Beginning in the 1970s, analytical chemistry ended up being gradually more inclusive of biological questions (bioanalytical chemistry), whereas it had formerly been mainly concentrated on inorganic or little organic particles.
Companies Leading The Way In Analytical Chemistry Testing
Modern analytical chemistry is controlled by important analysis. Many analytical chemists focus on a single type of instrument. Academics tend to either focus on new applications and discoveries or on new methods of analysis.
Many approaches, as soon as established, are kept intentionally fixed so that information can be compared over long periods of time. (QA), forensic and environmental applications.
The existence of copper in this qualitative analysis is shown by the bluish-green color of the flame Although contemporary analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and a few of the principles utilized in contemporary instruments are from conventional methods, a number of which are still used today. types of laboratories in the world.
Qualitative analysis figures out the existence or absence of a particular compound, but not the mass or concentration. By meaning, qualitative analyses do not measure quantity. Inorganic qualitative analysis typically refers to an organized plan to validate the existence of certain aqueous ions or components by performing a series of responses that eliminate a range of possibilities and then verify suspected ions with a verifying test.
Many of the major advancements in analytical chemistry took place after 1900. Throughout this duration, critical analysis ended up being gradually dominant in the field. In specific, many of the fundamental spectroscopic and spectrometric methods were discovered in the early 20th century and improved in the late 20th century.
I Changed My Mind About Set Laboratory. Here’s Why
In the 1970s much of these strategies began to be used together as hybrid techniques to achieve a complete characterization of samples. Starting in the 1970s, analytical chemistry became gradually more inclusive of biological questions (bioanalytical chemistry), whereas it had actually formerly been mostly concentrated on inorganic or little natural molecules.
The late 20th century likewise saw a growth of the application of analytical chemistry from rather academic chemical concerns to forensic, ecological, commercial and medical questions, such as in histology. Modern analytical chemistry is controlled by important analysis. Numerous analytical chemists concentrate on a single kind of instrument. Academics tend to either concentrate on brand-new applications and discoveries or on new approaches of analysis.
Lots of methods, as soon as developed, are kept intentionally static so that information can be compared over long periods of time. (QA), forensic and environmental applications.
The presence of copper in this qualitative analysis is indicated by the bluish-green color of the flame Although contemporary analytical chemistry is controlled by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and some of the concepts utilized in modern-day instruments are from standard techniques, a number of which are still utilized today.
Qualitative analysis figures out the existence or absence of a particular compound, however not the mass or concentration. By definition, qualitative analyses do not measure quantity (why is analytical chemistry important). Inorganic qualitative analysis usually refers to a methodical plan to confirm the presence of certain liquid ions or aspects by performing a series of responses that remove a variety of possibilities and then validate believed ions with a validating test.